Trauma Defined
The longer we live, the more inevitable it is that we will experience trauma. Trauma is the response to a deeply distressing or disturbing event that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope, causes feelings of helplessness, diminishes their sense of self and their ability to feel the full range of emotions and experiences.

It does not discriminate and it is pervasive throughout the world. A World Mental Health survey conducted by the World Health Organization found that at least a third of the more than 125,000 people surveyed in 26 different countries had experienced trauma. That number rose to 70% when the group was limited to people experiencing core disorders as defined by the DSM-IV (the classification found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition). But those numbers are just for instances that have been reported; the actual number is probably much, much higher.
While there are no objective criteria to evaluate which events will cause post-trauma symptoms, circumstances typically involve the loss of control, betrayal, abuse of power, helplessness, pain, confusion and/or loss. The event need not rise to the level of war, natural disaster, nor personal assault to affect a person profoundly and alter their experiences. Traumatic situations that cause post-trauma symptoms vary quite dramatically from person to person. Indeed, it is very subjective and it is important to bear in mind that it is defined more by its response than its trigger.
Taken from the article What is Trauma by By Karen Onderko, Director of Research and Education at Integrated Listening Systems.
Common Responses and Symptoms of Trauma
Response to a traumatic event varies significantly among people, but there are some basic, common symptoms.
Emotional signs include:
- sadness
- anger
- denial
- fear
- shame
These may lead to:
- nightmares
- insomnia
- difficulty with relationships
- emotional outbursts
Common physical symptoms:
- nausea
- dizziness
- altered sleep patterns
- changes in appetite
- headaches
- gastrointestinal problems
Psychological disorders may include:
- PTSD
- depression
- anxiety
- dissociative disorders
- substance abuse problems

What Trauma means in the classroom
Trauma is particularly challenging for educators to address because kids often don’t express the distress they’re feeling in a way that’s easily recognizable — and they may mask their pain with behavior that’s aggressive or off-putting. As Nancy Rappaport, a child and adolescent psychiatrist who focuses on mental health issues in schools, puts it, “They are masters at making sure you do not see them bleed.”
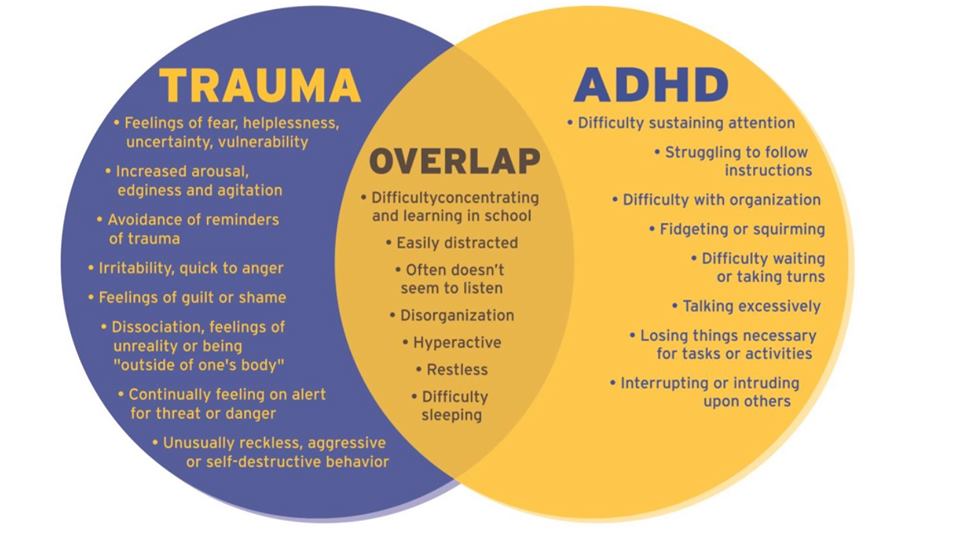
Identifying the symptoms of trauma in the children can help educators understand these confusing behaviors. And it can help avoid misdiagnosis, as these symptoms can mimic other problems, including ADHD and other behavior disorders.
In brief, the obstacles to learning experienced by these children include:
- Trouble forming relationships with teachers
- Poor self-regulation
- Negative thinking
- Hypervigilance
- Executive function challenges
Taken from the article How Trauma Affects Kids in School by Caroline Miller
For more information about how trauma affects students in the classroom, please take a look at the 8 minute video below by following the link.
Learning Brain vs Survival Brain Video: